When you’re eager to help your plants grow, it’s easy to think that more fertilizer will do the trick. However, adding too much can actually harm your crops and slow their progress.
Over-fertilizing can cause damage like burning plants or stunting their growth, which can lead to poor harvests. Knowing how excess fertilizer affects your garden helps you avoid common mistakes and keep your crops healthy.
Yellowing and wilting of lower leaves
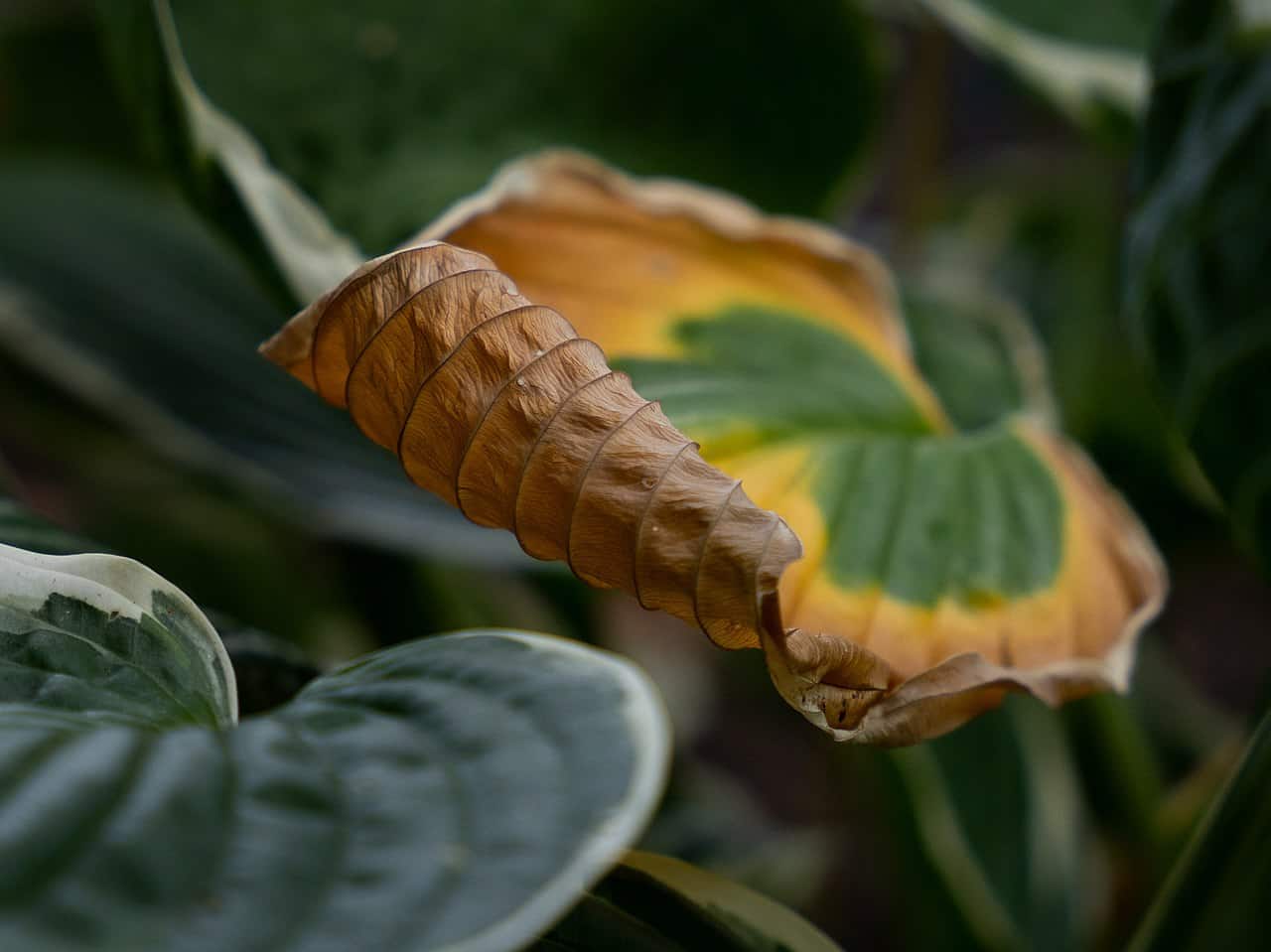

If you notice the lower leaves on your plants turning yellow and wilting, over-fertilizing might be the cause. Too much fertilizer can damage roots, limiting nutrient and water uptake.
This stress often shows first in older, lower leaves. You might also see brown tips or margins alongside the yellowing. Keep an eye on your fertilizer use to avoid this problem.
Browning leaf tips and margins

You might notice your plant’s leaf tips and edges turning brown when it’s getting too much fertilizer. This happens because over-fertilizing leaves behind salts that damage the leaf tissue.
If you see this, try cutting back on the fertilizer and flush the soil with water to remove excess salts. Your plant will thank you for the gentler treatment.
Browned or blackened limp roots
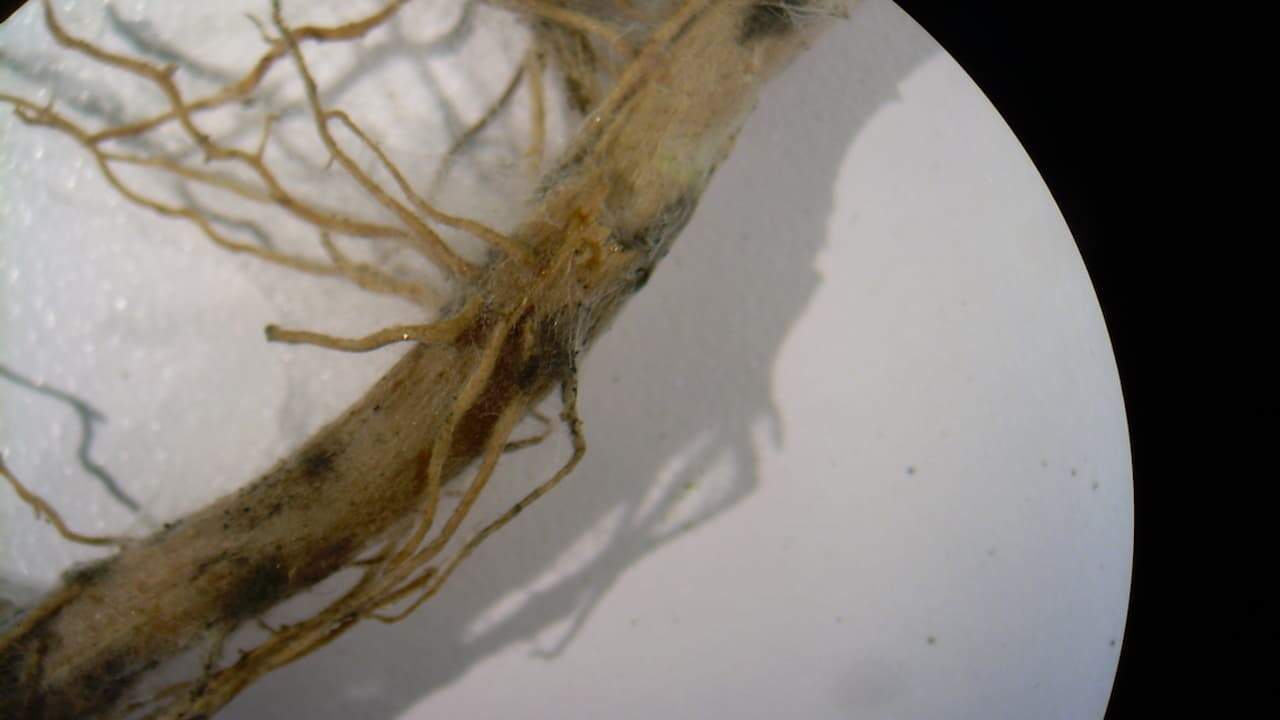
If you notice your roots turning brown or black and feeling limp, it’s a clear sign of over-fertilizing. Too much fertilizer can damage your roots by burning them, making it hard for your plants to absorb water and nutrients.
This root damage often shows alongside yellowing or wilting leaves. To help your plants, you can gently flush the soil with water to remove excess fertilizer and protect those delicate roots.
Crust of fertilizer on soil surface

You might notice a hard crust forming on the surface of your soil after over-fertilizing. This crust can prevent water from soaking in properly, making it harder for your plants to get the moisture they need.
If you see this crust, gently remove it without disturbing too much soil. Doing so helps your plants breathe and absorb nutrients better.
Sudden rapid growth with weak roots

When you over-fertilize, your plants might grow fast above ground, but their roots can stay weak. This sudden growth looks healthy at first, but the roots don’t develop enough strength to support it.
Weak roots make your plants less stable and more likely to suffer damage from wind or storms. Over time, this can reduce your crop’s overall health and yield.
Nutrient burn causing leaf burn
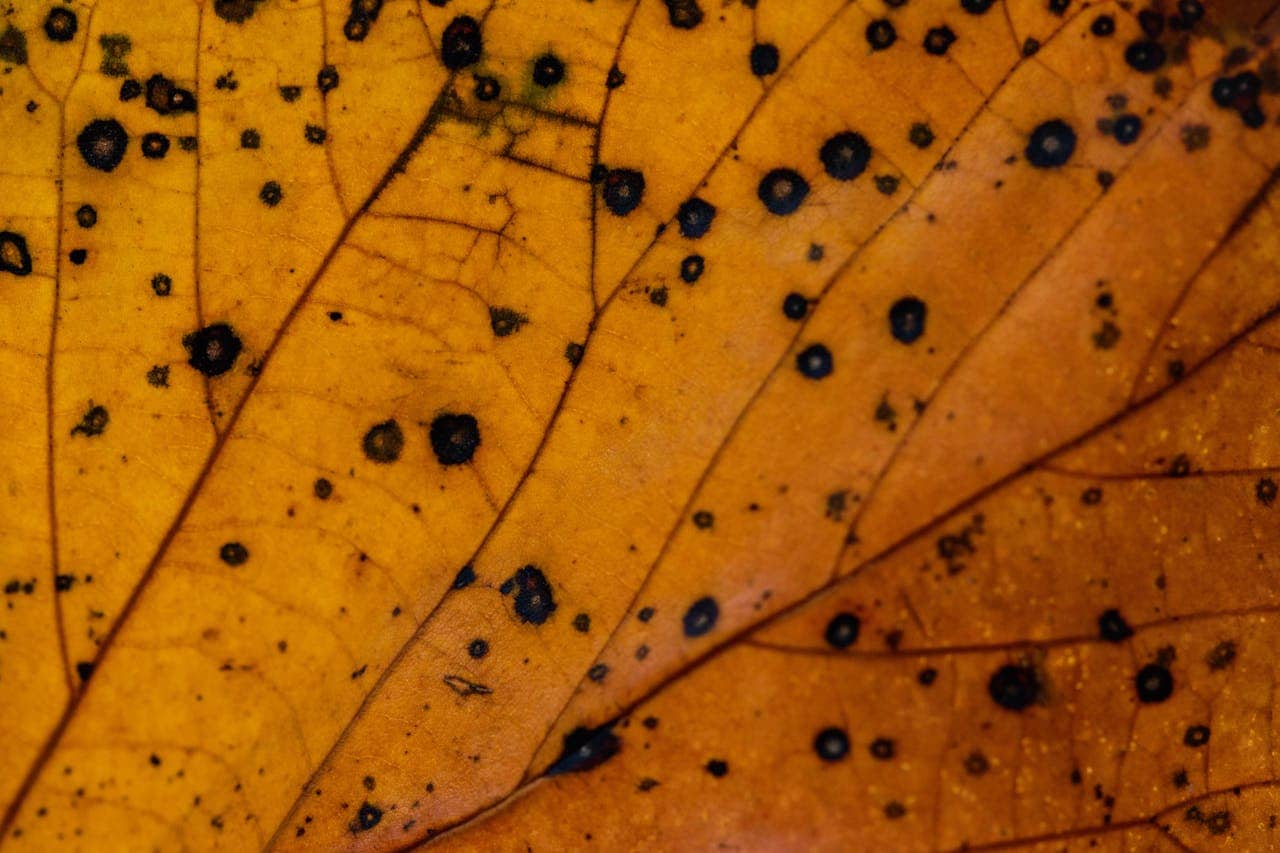

When you over-fertilize your crops, the excess nutrients can cause nutrient burn. This often shows up as leaf burn, where the edges become brown, crispy, or curled.
You might notice yellowing or dark spots on the leaves. These are signs your plants are stressed from too many nutrients.
If this happens, try flushing the soil with water to remove the excess fertilizer. This can help your plants recover and prevent further damage.
Reduced fruit and vegetable yield

When you over-fertilize your crops, it can actually harm their growth. Too much fertilizer may cause your plants to focus on leaves instead of fruits or vegetables.
This can lead to fewer fruits or vegetables developing, lowering your overall yield.
Excess nutrients can also cause stress to your plants, making them more vulnerable to pests and diseases, which further reduces your harvest.
Soil nutrient imbalance

When you over-fertilize, your soil’s nutrient balance can get thrown off. Too much of one nutrient might block your plants from absorbing others they need.
This imbalance can slow down your plants’ growth and make them weaker. Keeping nutrients in the right amounts helps your crops stay healthy and strong.
Toxic buildup harming beneficial microbes

When you over-fertilize, harmful chemicals can build up in your soil. This toxic buildup damages the beneficial microbes that help your plants grow strong.
These microbes support nutrient cycling and protect your crops from diseases. Without them, your soil becomes less healthy, and your plants may suffer. Taking care with fertilizer amounts helps keep these helpful microbes safe.
Stunted root development

When you over-fertilize, your plants may grow fast above ground but their roots struggle to keep up. This happens because too many nutrients can overwhelm the root system.
Your roots can become weak and stunted, limiting water and nutrient uptake. Without strong roots, your crops won’t thrive even if the leaves look healthy.
Excess fertilizer causes salt buildup around roots, which can damage them and stunt growth further. Be careful not to overfeed your soil to avoid this.
Lower plant resistance to diseases

When you over-fertilize, your plants can become weaker and less able to fight off diseases. Excess nutrients can disrupt the natural balance of microbes on leaves, which normally protect your plants.
Too much fertilizer also stresses plants, making them more attractive to insects that spread disease. Keeping the right fertilization helps your plants stay healthy and strong against infections.
Leaching of nutrients into groundwater

When you apply too much fertilizer, nutrients like nitrogen can seep below the plant roots. This process, called leaching, moves those nutrients into the groundwater.
Leached nutrients stay in soil and water for decades, slowly affecting water quality. This can cause problems like harmful algal blooms in nearby lakes and rivers.
To protect your crops and the environment, try to use the right fertilizer amount and avoid over-watering. This helps keep nutrients where your plants can use them.
Plant dehydration despite watering

You might water your crops regularly but still see signs of dehydration. Over-fertilizing increases the salt concentration in the soil, making it harder for plants to absorb water.
This creates a drought-like effect even when the soil is moist. Your plants can look thirsty because their roots struggle to take up enough water.
To help, flushing excess nutrients with clean water can restore balance. This way, your plants can absorb water more effectively and recover from dehydration.
